Part of a solar/UPS (uninterrupted power supply) system is the batteries that are used to store the energy from either solar panels, or the grid so it can be used when other power sources are not present, or not sufficient.
Among the different LiFeP04 pack configurations, both a 15-cell 48V pack and a 16-cell 51.2V pack are commonly used. A 16-cell LiFeP04 51.2V pack offers superior performance compared to that of a 15-cell 48V pack with the same grade cells as the 16-cell pack.
What is the difference between a 15-cell and 16-cell battery pack?
What is the difference between a 15-cell 48V battery pack and a 16-cell 51.2V battery pack (like the REVOV R100 battery) with the same quality of cells?
The differences between a 15 and 16-cell battery pack are shown in the table below. For comparison, cells with the same grade, nominal voltage (3.2 V), and capacity (100Ah/320Wh) have been used.
| 15 Cell | 16 Cell | |
| Nominal Voltage | 48 V | 51.2 V |
| Lower Cut-off voltage | 45 V | 48 V |
| Absorption voltage | 52 V | 55.5 V |
| Pack Capacity | 4.8 kWh | 5.12 kWh |
As shown, the total capacity of a 16-cell battery is more than a 15-cell battery, as is the nominal voltage which offers a small improvement in the efficiency at which the inverter can convert the DC to AC. While the values in the table are theoretical, it is not the same in practice, as the 15-cell battery packs recommend an operating voltage range that is often larger, thus placing more strain on the individual cells resulting in decreasing lifespans and performance. The performance of the packs also depends on the BMS, the quality of the cells, the capacity of the cells, and the cell pairing.
How do I know how many cells are in the battery pack?
It is often not advertised how many cells a battery pack has, however the nominal voltage as well as the voltage operating range must be provided. To calculate the number of cells in a battery pack, you can divide the nominal voltage of the battery pack by the nominal voltage of a cell to calculate the number of cells, e.g.: The number of cells in a 51.2V nominal voltage battery pack.
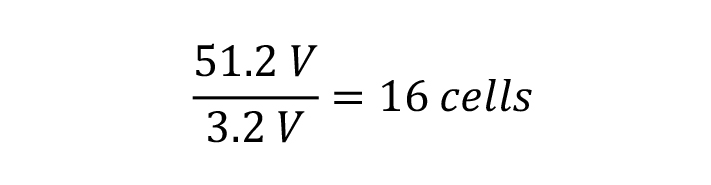
The calculation is based on a series of battery cells with a nominal voltage of 3.2V each.
In conclusion
A 16-cell battery is superior to a 15-cell battery in terms of capacity, as it contains an extra cell. The REVOV 16-cell batteries also recommend voltage ranges that (when set up correctly) ensure maximum performance and lifespan of your REVOV battery. REVOV 16-cell batteries (such as the R100 and R9 batteries) also make use of extremely high-grade 2ndLiFe LiFePo4 batteries. Such high-grade cells offer superior performance to storage-grade cells commonly used in backup systems.
Deep Cycle Batteries: Comparing Lead-Acid and Lithium-Ion Batteries
If you’re considering investing in deep cycle batteries, it’s essential to understand what they are and how they work. You also need to know the differences between lead-acid and lithium-ion deep cycle batteries. In this article, we explain: what deep cycle batteries...
Switching inverters vs coil-based inverters
Summary Over the past decade inverter technology in the renewable energy sector has made strides. Currently the most common types of inverters include both coil-based and switching inverters. Both have their uses and benefits when compared against each other....
REVOV Information Series: Sizing a system: Batteries and Inverter
The design of a solar system before purchasing and installation requires knowledge of the premises and usage of the system, which inverters would be appropriate, as well as the sizing of the energy storage capacity based on the inverter’s maximum delivery. The...





Recent Comments